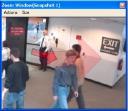
 The International Business Times is running a report on the future of surveillance cameras. The latest generation of surveillance cameras are aiming to provide a greater degree of video analysis in order to ease the burden of conventional human based video monitoring. Using algorithms to monitor crowd movement or suspicious behaviour, human operators can be alerted faster to potential problems.
The International Business Times is running a report on the future of surveillance cameras. The latest generation of surveillance cameras are aiming to provide a greater degree of video analysis in order to ease the burden of conventional human based video monitoring. Using algorithms to monitor crowd movement or suspicious behaviour, human operators can be alerted faster to potential problems.
Read the rest of this entry »
Surveillance Cameras Get Smarter
Automatic Facial Animation Analysis
A number of recent research projects have been focusing their attentions to the open-ended problem of generating realistic facial animations from 3D head models. Initially we discuss the motivation for researching automated facial animation methods. Secondly we investigate a variety of traditional and cutting edge approaches to the problem.
3D Reconstruction and Recognition
Accepted for publication in: Biometric Technology for Human Identification IV 2007
Download: 3D Reconstruction and Recognition (pdf)
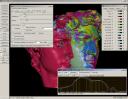
In this paper we propose a novel 3D face recognition system. Furthermore we propose and discuss the development of a 3D reconstruction system designed specifically for the purpose of face recognition. The reconstruction subsystem utilises a capture rig comprising of six cameras to obtain two independent stereo pairs of the subject face during a structured light projection with the remaining two cameras obtaining texture data under normal lighting conditions. Whilst the most common approaches to 3D reconstruction use least square comparison of image intensity values, our system achieves dense point matching using Gabor Wavelets as the primary correspondence measure.
Read the rest of this entry »
Scanalyze
OpenCV
An excellent and fully featured computer vision library. OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision) is a library of programming functions mainly aimed at real time computer vision.
Example applications of the OpenCV library are Human-Computer Interaction (HCI); Object Identification, Segmentation and Recognition; Face Recognition; Gesture Recognition; Motion Tracking, Ego Motion, Motion Understanding; Structure From Motion (SFM); and Mobile Robotics.
Xface
Xface is an open source toolkit implementing the MPEG-4 standard for facial animation.
Main Features:
* Accepts MPEG-4 FAP files and SMIL-Agent scripts as input.
* Supports muscle based deformation (for MPEG-4) and keyframe based animation using morph targets.
* Muscle deformation methods/rules can be extended easily.
* Blending of visemes (visual phonemes), emotions, expressions.
* Head and eye movements (random and controlled).
* Can use various TTS engines using the pluggable factory mechanism.
* Control over TCP/IP. XfacePlayer can be controlled using any programming language thanks to our messaging system.
* Save animation as video in avi format.
* Platform independent code. (We distribute only windows version, however people reported compiling it under Linux successfully)
Read the rest of this entry »
Bionic eye offers hope of restored vision
A new bionic eye could restore vision to the profoundly blind. A prototype was tested on six patients and ‘within a few weeks all could detect light, identify objects and even perceive motion again. For one patient, this was the first time he had seen anything in half a century.’ The user wears a pair of glasses that contain a miniature camera and that wirelessly transmits video to a cellphone-sized computer in the wearer’s pocket. This computer processes the image information and wirelessly transmits it to a tiny electronic receiver implanted in the wearer’s head.
Read the full article here
This story was covered on slashdot here.
Mimicking How the Brain Recognizes Street Scenes
 Researchers at the MIT McGovern Institute for Brain Research have used a biological model to train a computer model to recognize objects, such as cars or people, in busy street scenes. Their innovative approach, which combines neuroscience and artificial intelligence with computer science, mimics how the brain functions to recognize objects in the real world. This versatile model could one day be used for automobile driver’s assistance, visual search engines, biomedical imaging analysis, or robots with realistic vision.
Researchers at the MIT McGovern Institute for Brain Research have used a biological model to train a computer model to recognize objects, such as cars or people, in busy street scenes. Their innovative approach, which combines neuroscience and artificial intelligence with computer science, mimics how the brain functions to recognize objects in the real world. This versatile model could one day be used for automobile driver’s assistance, visual search engines, biomedical imaging analysis, or robots with realistic vision.
Here is the original paper (pdf)
-
You are currently browsing the Daniel Bardsley blog archives for February, 2007.